What is a Local Area Network (LAN)?
A local area network (LAN), is a computer networking solution that connects devices in a limited area, such as a building, office, home and even campuses of adjacent buildings. In contrast, a wide area network (WAN) covers larger geographic areas.
Architecturally, a local area network (LAN) can be set up in two ways:
- A Peer-to-peer LAN directly connects two devices.
- A Client-server LAN – is typical in business environments and includes multiple endpoints and servers connected to a LAN switch that directs communication among devices.
What is a Wired Local Area Network?
A wired LAN includes a switch that uses Ethernet cabling to connect to servers, workstations and other endpoints to the corporate network.
Example of a Wired Local Area Network
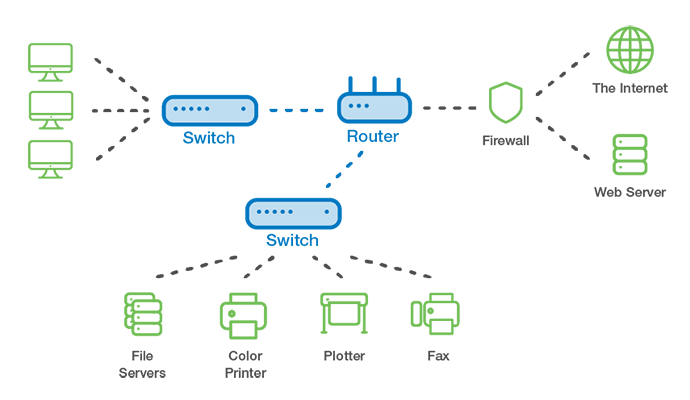
What is a Virtual Local Area (VLAN) Network?
Smaller organizations with only a few devices can usually get by with a wired LAN, including one switch with Ethernet ports to interconnect all devices.
However, larger organizations with hundreds or thousands of devices require additional hardware, software and configuration to form multiple virtual LANs (VLANs).
VLANs limit the amount of traffic individual devices experience, alleviating network congestion and bottlenecks that impact network performance.
Example of a Virtual Local Area Network
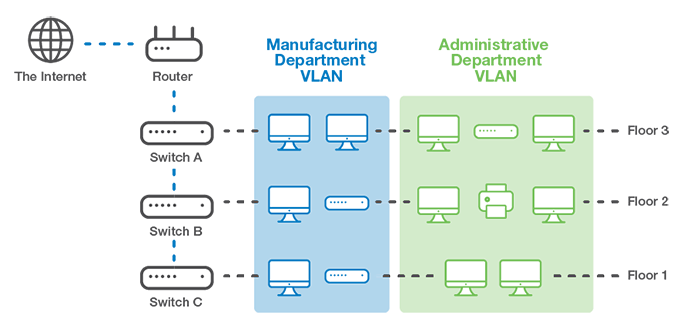
What is a Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)?
A wireless local area network (WLAN) is identical to a wired LAN except that the devices that make up the network are connected through radio transmissions, typically a Wi-Fi signal, instead of wired connections. An office or home Wi-Fi network is considered a WLAN.
A WLAN typically consists of a wireless router and endpoints, such as computers, mobile devices, printers, fax machines and other devices. The wireless router enables the devices to talk to each other and also connect to the Internet.
The ease of setup and management has made WLANs commonplace in offices that rely heavily on smartphones, tablets and other mobile devices. But it also has made it possible for other types of businesses, such as restaurants, coffee shops and stores, to have a WLAN. Wi-Fi also has expanded the types of connected devices beyond desktops and printers to include smart devices like lighting, thermostats, security cameras and more.
Example of a Wireless Local Area Network
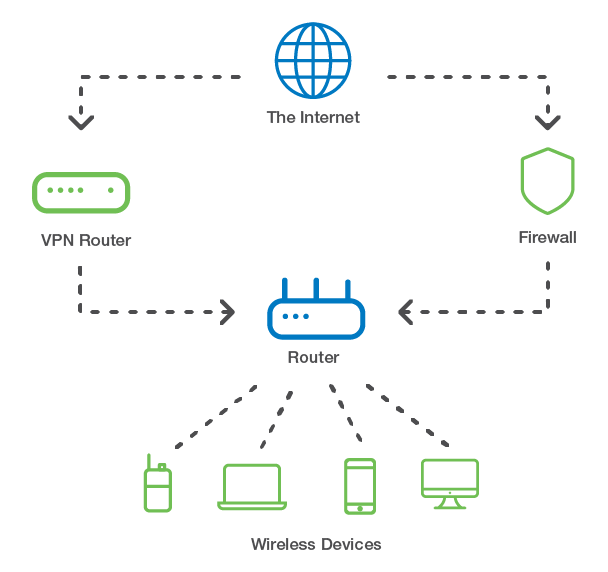
Wireless LAN vs. Wired LAN
Traditionally, companies with high security and bandwidth requirements have preferred wired LANs, while those that require mobility have chosen wireless options. With advances in wireless technologies, most organizations now use wireless LANs, at least in part. Here’s why:
|
Wireless LAN Wireless LANs have these advantages over wired LANs: |
|---|
|
Convenience Wireless LANs are easier to set up when compared to wired LANs since they don’t require cabling. |
|
Flexibility Endpoint devices like computers and printers only need to be in the wireless signal range and aren’t tethered to the wire connection. |
|
Mobile Access Employees can connect to a wireless LAN through smartphones and tablets, which is impossible with wired LANs. |
|
Wired LAN Wired LANs have these advantages over wireless LANs: |
|---|
|
Speed Wired LANs support greater bandwidth and have faster connection speeds. |
|
Reliability Weak signal strength common with wireless LANs is not an issue with wired LANs. |
|
Greater Security To break into a wired LAN, the hacker must connect to a network switch, router or computer before accessing the network. |
Have more questions about networking solutions?
We can help! Get in touch with us below to speak to one of our experts.
"*" indicates required fields
